La Niña: A Cool Phase with Global Impacts
The upcoming months are anticipated to be influenced by La Niña, a climatic trend that affects the weather worldwide. Find out how it affects temperature, rainfall, and tropical cyclones. Keep abreast of the most recent predictions and scientific discoveries.
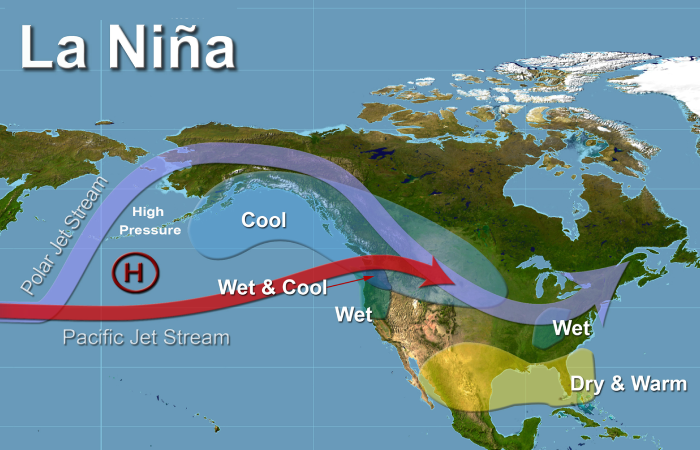
With its origins in the tropical Pacific Ocean, La Niña is a complex climatic trend that is predicted to affect global weather patterns. Known for its lower-than-normal sea surface temperatures, this natural phenomenon has a big impact on a lot of different areas of the world.
This article will discuss La Niña's details, potential impacts on global weather patterns, and the latest scientific findings on this intriguing climate cycle.
What is La Niña?
Originating in the tropical Pacific Ocean, La Niña is a complicated climate phenomenon that is frequently referred to as the "cool phase" of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle. The tropical Pacific Ocean's eastern and central surface waters get colder than usual during a La Niña event. Weather systems around the world are impacted by this cooling, which throws off regular patterns of air pressure.
La Niña's Impact on Global Weather Patterns
La Niña occurrences have a major effect on global weather patterns. A list of some of the primary consequences is provided below:
Patterns of Rainfall:
- Increased precipitation: The Pacific Northwest and some regions of South America frequently get higher rainfall during La Niña.
- Reduced precipitation: In contrast, it can result in drier weather in parts of the southern United States, Southeast Asia, and Australia.
Temperature Patterns:
- Lower temperatures: Particularly in the winter, La Niña can result in lower-than-normal temperatures in the northern United States and Canada.
- Warmer temperatures: Conversely, it might result in warmer-than-normal temperatures in parts of South America and the southern United States.
Tropical Cyclones:
- Increased activity: La Niña has the potential to cause more hurricanes in the Atlantic basin.
- Decreased activity: In the eastern Pacific, it can inhibit hurricane activity.F

La Niña News and Updates for the Coming Months
There is a high probability that La Niña will form in the upcoming months as of December 2024. The most recent updates are as follows:
WMO News:
- There is a 60% possibility that La Niña will form by the end of 2024, according to the World Meteorological Organization (WMO).
- Forecasts from the WMO Global Producing Centers of Long-Range Forecasts served as the basis for this projection.
- It is thought that there is very little likelihood of El Niño emerging during this time.
Climate Prediction Center of NOAA:
- Additionally, according to the NOAA Climate Prediction Center, there is a substantial chance that La Niña will form in October–December 2024 and last until January–March 2025.
- Sea surface temperatures as well as other oceanic and atmospheric factors were analyzed to make this prediction.
One should keep in mind that La Niña occurrences can differ in strength and duration. Even though there is a high chance of La Niña according to current forecasts, the precise effects on your area may vary.
The most recent predictions from reputable organizations, such as the WMO and the NOAA Climate Prediction Center, should be kept up to date.
Understanding the possible effects of La Niña allows people, communities, and governments to prepare ahead and take the appropriate preparations to minimize dangers and maximize benefits.
Scientific Discussions on La Niña
The intricacies of La Niña and its effects on the world are still being explored by scientists. Among the main topics of scientific discourse are:
Predictability: One of the main areas of research is increasing the precision of La Niña forecasts. More complex models that can more accurately forecast the beginning, severity, and length of these catastrophes are being developed by scientists.
Teleconnections: Predicting regional climate impacts requires an understanding of the long-distance atmospheric and oceanic interconnections, or teleconnections, that exist between the tropical Pacific and other regions.
Climate Change: There is continuous discussion over how climate change affects La Niña. While some studies contend that the influence of climate change is minimal, others believe that it may change the frequency and intensity of La Niña episodes.
Socioeconomic Impacts: Scientists are investigating how La Niña will affect public health, agriculture, and fisheries, among other socioeconomic factors.
Conclusion
La Niña is a complicated climate event that affects worldwide weather patterns in a big way. Understanding its dynamics is crucial for minimizing its possible hazards and optimizing its chances, even if it can have both positive and negative effects.
We should anticipate a better knowledge of La Niña's influence on the climate of our world as researchers strive to solve its riddles.




